- Email: info@crystaleyesclinicwakad.com
- Wakad, Pune
- Call: +91 9767443270
Services/Treatments
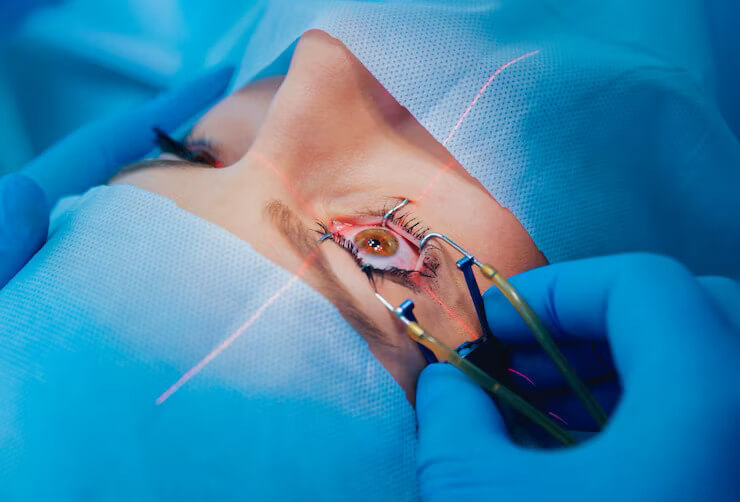
Cataract Surgery
Cataract surgery, also called lens replacement surgery, is the removal of the natural lens of the eye (also called "crystalline lens") that has developed an opacification, which is referred to as a cataract, and its replacement with an intraocular lens. Metabolic changes of the crystalline lens fibers over time lead to the development of the cataract, causing impairment or loss of vision. Some infants are born with congenital cataracts, and certain environmental factors may also lead to cataract formation. Early symptoms may include strong glare from lights and small light sources at night, and reduced acuity at low light levels.
Well over 90% of operations are successful in restoring useful vision, with a low complication rate. Day care, high volume, minimally invasive, small incision phacoemulsification with quick post-op recovery has become the standard of care in cataract surgery all over the world.
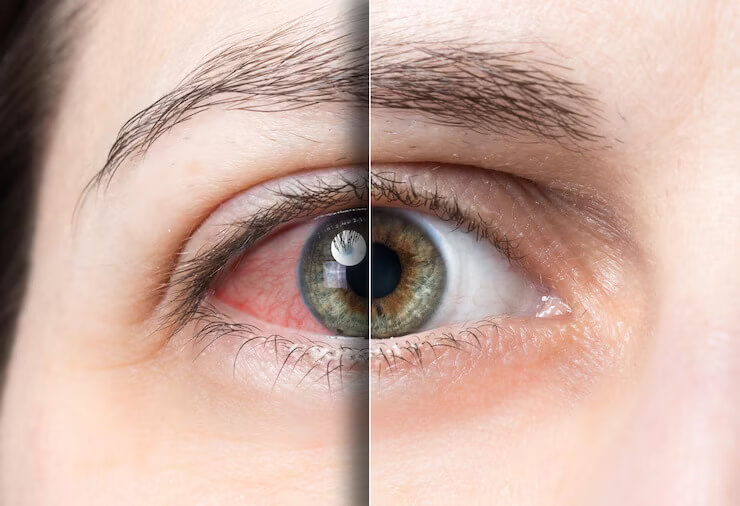
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that damage the optic nerve. The optic nerve sends visual information from your eye to your brain and is vital for good vision. Damage to the optic nerve is often related to high pressure in your eye. But glaucoma can happen even with normal eye pressure.
The most common type of glaucoma (open-angle glaucoma) often has no symptoms other than slow vision loss. Angle-closure glaucoma, although rare, is a medical emergency and its symptoms include eye pain with nausea and sudden visual disturbance. Treatment includes eye drops, medication and surgery. There is no cure (yet) for glaucoma, but if it's caught early, you can preserve your vision and prevent vision loss. Taking action to preserve your vision health is key.
Lasik Laser Surgery
LASIK or Lasik, commonly referred to as laser eye surgery or laser vision correction, is a type of refractive surgery for the correction of myopia, hyperopia, and an actual cure for astigmatism, since it is in the cornea.LASIK surgery is commonly performed laser refractive surgery to correct vision problems.
The main goal of LASIK eye surgery is to change the shape of the cornea so that it can better focus images onto the retina, allowing you to see more clearly. This effect is achieved through the use of two lasers.

Squint Eye Surgery
The surgeon detaches part of the muscle connected to the eye and moves it into a new position so that the eyes point in the same direction. the muscles are fixed in their new position with dissolvable stitches – these are hidden behind the eye so you will not be able to see them afterwards.
Surgery can help improve the alignment of the eyes even if a squint has been left untreated for a long time, but any vision problems may be permanent if they are not treated at a young age.
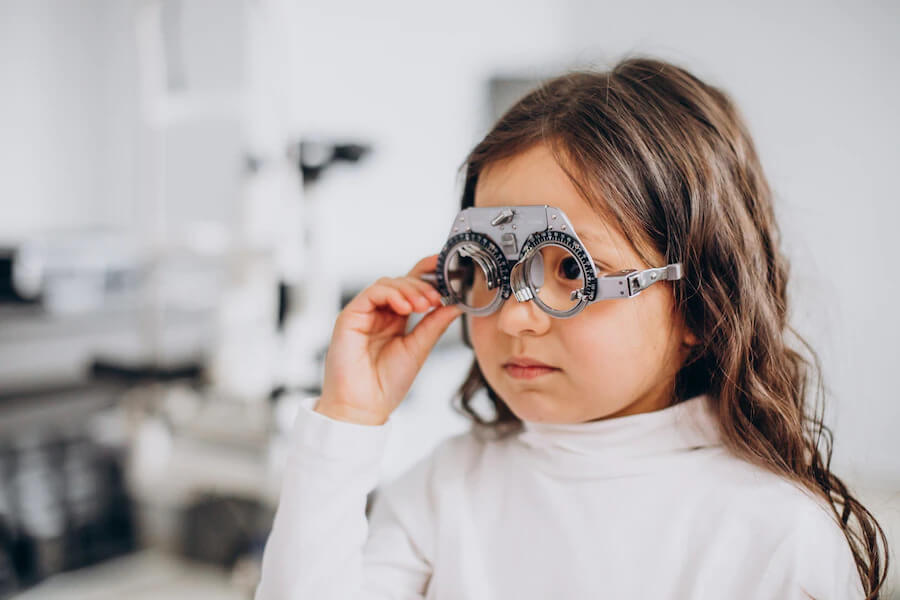

Paediatric Ophthalmology
Paediatric ophthalmologists can diagnose, treat, and manage all children's eye problems.
Paediatric ophthalmology is a subspecialty of ophthalmology that concentrates on treating the various eye problems affecting children. Studies show that a lot of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and learning issues in children can be attributed to vision problems.
Eye Retina Treatment
Retina specialists are ophthalmologists that have completed training (including a one- or two-year fellowship) after their three year ophthalmology residency to specialize in diseases and conditions related to the vitreous and retina.
Laser surgery can repair a retinal tear or hole. Your surgeon uses a laser to heat small pinpoints on the retina. This creates scarring that usually binds (welds) the retina to the underlying tissue. Immediate laser treatment of a new retinal tear can decrease the chance of it causing a retinal detachment.
Refractive Eye Surgery
Laser eye surgery is the most commonly practiced procedure to correct vision problems caused by refractive errors, including myopia (near-sightedness), hyperopia (far-sightedness) and astigmatism (distorted vision when looking at objects at any distance).
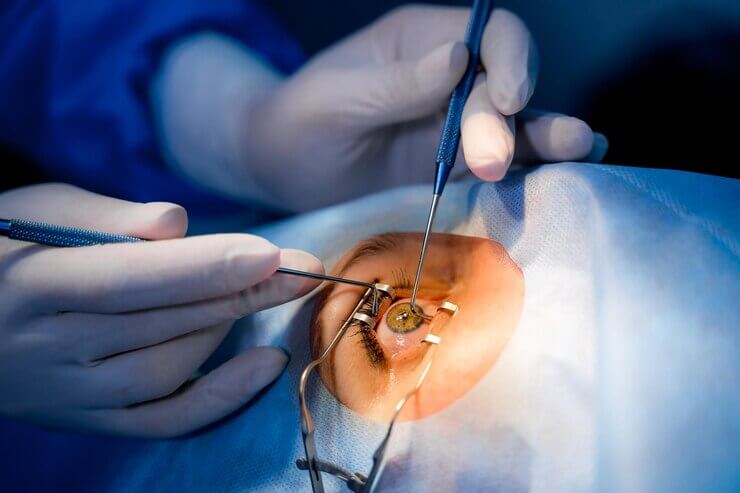
Cornea Eye Surgery
A cornea transplant is most often used to restore vision to a person with a damaged cornea. A cornea transplant also can relieve pain or other symptoms associated with cornea diseases. A number of conditions can be treated with a cornea transplant, including: A cornea that bulges outward, called keratoconus.
During this procedure, a circular piece of damaged cornea from the centre of your eye is removed and replaced with the donated cornea. In most cases, a circular cutting instrument (similar to a cookie cutter) called a trephine is used to remove the damaged cornea.
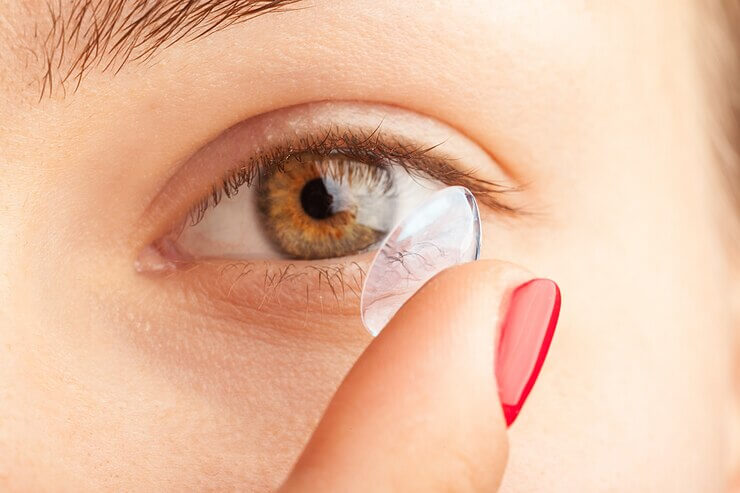
Contact Lens
They produce a more “natural” field of vision.
Because they sit on the surface of your eyes and move with them, contact lenses provide seamless vision correction. Their benefits extend to your peripheral vision and they won't have the same types of visual disruptions that glasses do, such as reflections or fogginess.
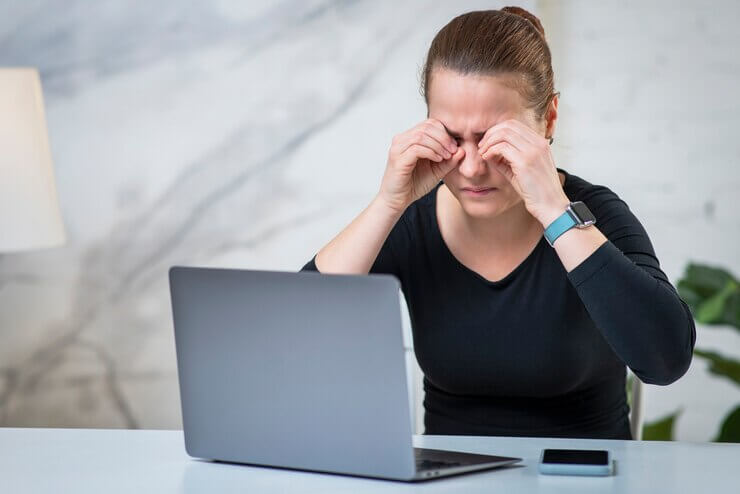

Computer Vision Syndrome
Computer Vision Syndrome is the name given to eye problems caused by prolonged computer use including: Eye irritation (Dry eyes, itchy eyes, red eyes) Blurred vision. Headaches. Backaches.
Computer vision syndrome (CVS) has an ominous ring because it is a serious type of repetitive strain injury that affects your vision, along with other aspects of your physical health. The condition is also called digital eye strain.
Oculoplasty Eye Surgery
An oculoplastic procedure is a type of surgery done around the eyes. You may have this procedure to correct a medical problem or for cosmetic reasons. Oculoplastic procedures are usually done by eye doctors (ophthalmologists) who have special training in plastic or reconstructive surgery.
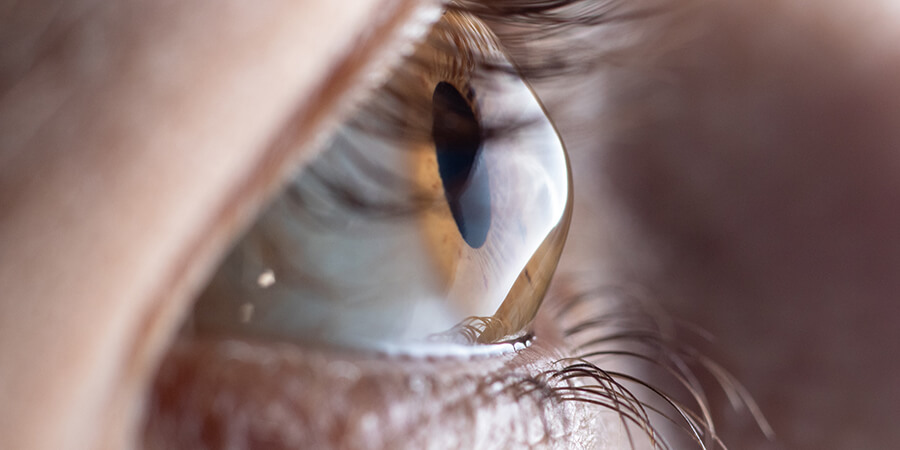

Keratoconous
A condition in which the clear tissue on the front of the eye (cornea) bulges outward.
With keratoconus, the clear, dome-shaped tissue that covers the eye (cornea) thins and bulges outward into a cone shape. Its cause is unknown. Symptoms first appear during puberty or the late teens and include blurred vision and sensitivity to light and glare.
Vision can be corrected with glasses or contact lenses early on. Advanced cases may require a cornea transplant.
Diabetic Retinopathy
A complication of diabetes that affects the eyes.
Diabetic retinopathy is caused by damage to the blood vessels in the tissue at the back of the eye (retina). Poorly controlled blood sugar is a risk factor. Early symptoms include floaters, blurriness, dark areas of vision and difficulty perceiving colours. Blindness can occur.
Mild cases may be treated with careful diabetes management. Advanced cases may require laser treatment or surgery.
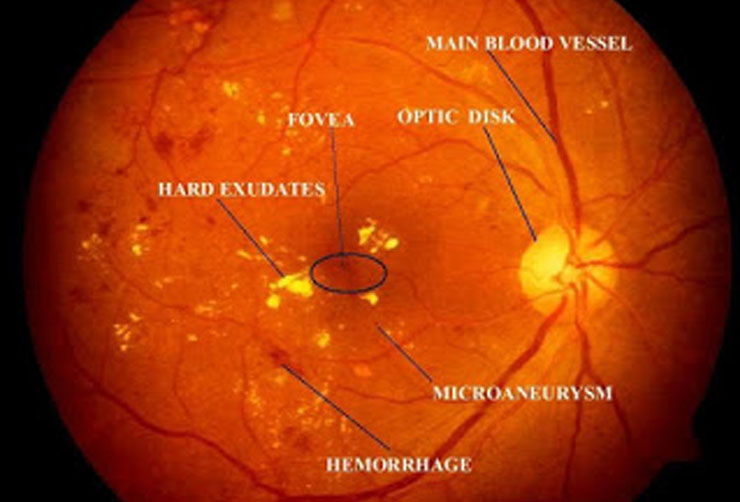
Diabetic and hypertensive retinal examination
Because your retina can be severely damaged before any change in vision is noticed, it is highly recommended that diabetic eye exams are performed on an annual basis. Hypertensive retinopathy is a condition in which there are changes in the retina due to high blood pressure.
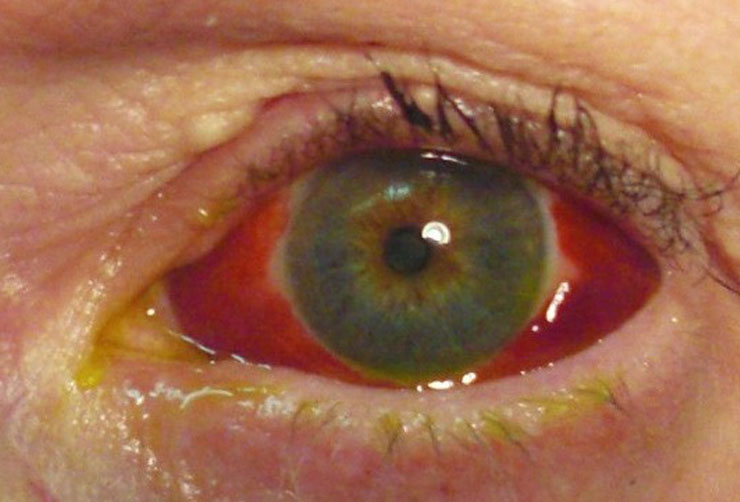
Conjunctivitis / Corneal Ulcer
Corneal ulcers are most commonly caused by an infection with bacteria, viruses, fungi, or a parasite. Acanthamoeba keratitis occurs in contact lens users. It is more likely to happen in people who make their own homemade cleaning solutions. Fungal keratitis can occur after a corneal injury involving plant material.

Sports Vision Tests and Training
Sports vision tests and training help athletes determine how well their eyes perform, beyond a basic ability to see letters and objects clearly on a standard eye chart.
- Hand-eye coordination, which helps athletes — including baseball players at bat — anticipate and hit a fast-moving ball.
- Improved depth perception to aid athletes such as downhill skiers when they negotiate turns and avoid obstacles.
- Eye tracking ability, which includes following and anticipating motion of a bouncing basketball.

Low visual aids vision rehabilitation
Low vision and blindness are a growing health problem that adversely affects the quality of life of an individual. Low vision rehabilitation (LVR) is the process of restoring functional ability and improving quality of life and independence of a patient with low vision. Currently India is a home to around one-third to one-fourth of the world’s blind population. Lack of awareness about the low vision services are a major drawback in the rehabilitation of a low vision patient in our country. Thus, in this article we discuss about the methods of evaluation of a patient with low-vision and prescription of low vision aids.
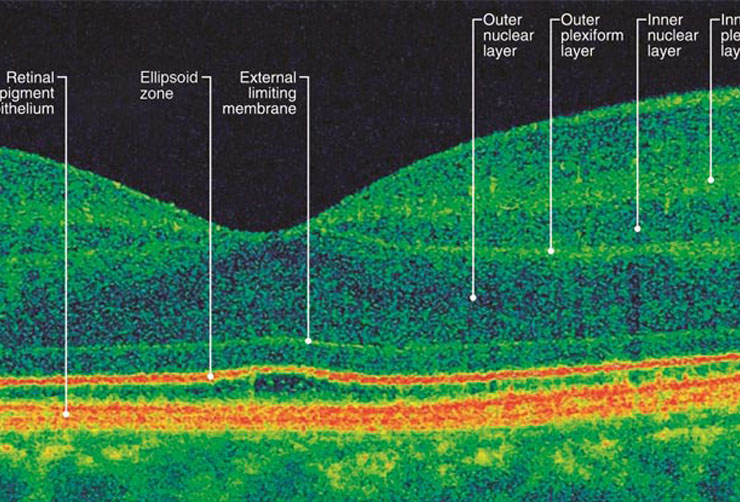
OCT
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging test. OCT uses light waves to take cross-section pictures of your retina.
With OCT, your ophthalmologist can see each of the retina’s distinctive layers. This allows your ophthalmologist to map and measure their thickness. These measurements help with diagnosis. They also provide treatment guidance for glaucoma and diseases of the retina. These retinal diseases include age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and diabetic eye disease.
